|
Natural Resources |
|
|
Bioactivities |
|
|
Identification |
Melting point |
>400°C |
1HNMR

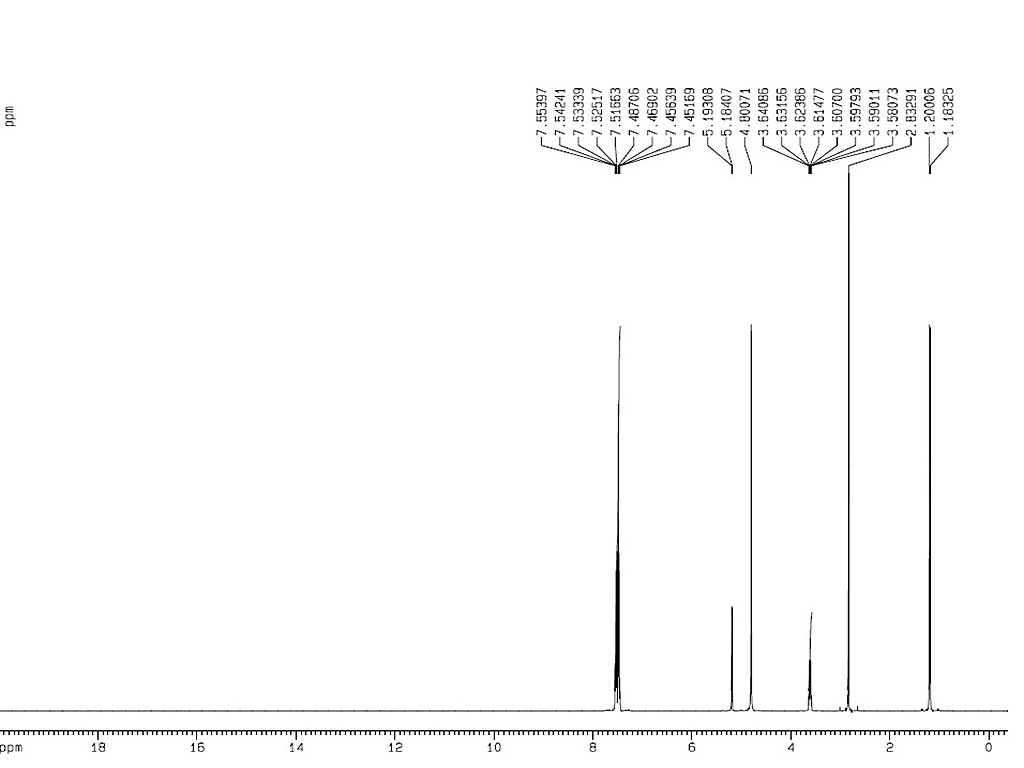
|
| Analytical Method |
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Silica gel 60F plates (Merck) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
Dichloromethane: hexane: methanol = 7: 4: 0.3, v/v/v |
| DETECTION |
Compare with commercial standard |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system (Agilent technologies Inc., Waldbronn, Germany) |
| COLUMN |
Thermo Hypurity-Advence C18 (5 μm, 250 mm × 3 mm i.d.) (USA) column and a Phenomenex Luna Security Guard Cartridge C18 (5 μm, 4 mm × 2.0 mm i.d.) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: water with 0.005% trifluoroacetic acid TFA, B: ACN containing 0.005% TFA, 0min 60% A, 0-25min 50% A, after elution the column was washed: 10 min 100% B, 7 min 60% A, 0.4 mL/min |
| DETECTION |
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) source on a quadrupole ion trap instrument (Thermo Finnigan LCQ, San Jose, CA, USA), Positive ion mode; sheath gas: 0.3 L/min; aux gas: 0 L/min, discharge: 5.5 μA, Vaporization temperature: 575°C, capillary: 200°C, capillary: 10 V, tube lens offset: 0 V, injection time: 500 ms |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
ACQUITY UPLC™ system (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) |
| COLUMN |
Waters UPLC HSS T3 column (100 mm × 2.1 mm i.d.; 1.8 μm) (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 0.1% Formic acid in water, B: 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile, 0-0.5 min 2% B, 0.5-2 min 2-100% B, 2-2.5 min 100% B, 2.5-2.6 min 100-2% B, 2.6-4 min 2% B, 0.5 mL/min |
| DETECTION |
Capillary voltage: 3.5 kV, 150°C ; Cone voltage: 47 V, 400°C ; collision energy: 20 eV; multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, 0.161 s |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1100 liquid chromatography system (Agilent technologies Inc., Waldbronn, Germany) |
| COLUMN |
Thermo Hypurity-Advence C18 (5 μm, 250 mm × 3 mm i.d.) (USA) column and a Phenomenex Luna Security Guard Cartridge C18 (5 μm, 4 mm × 2.0 mm i.d.) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 0.1% Formic acid in water, B: 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile, 0-0.5 min 2% B, 0.5-2 min 2-100% B, 2-2.5 min 100% B, 2.5-2.6 min 100-2% B, 2.6-4 min 2% B; 0.5 mL/min |
| DETECTION |
Positive ionization mode (ESI+), 25 L/h and 1000 L/h, Argon, collision gas 5.0 × 10−3 mbar, capillary voltage of 3.5 kV, 150°C, desolvation: 400°C, cone voltage: 47 V, collision energy: 20 eV |
|
| Sample Preparation |
|
METHOD 1 |
|
|
Extracted three times with 70% ethanol (EtOH) by sonication for 3 hours. Dried and loaded onto a Daion HP-20 open column (100 cm 10 cm; the volume of the column was 7.8 L) and sequentially eluted with a methanol gradient beginning with 100% water and increasing to 30, 65 and finally 80% methanol. 80 g high polar compounds (sugar) were eluted with water and 30% MeOH. Enriched ginsenoside fractions were eluted with 65% methanol (PPT 1.9 g) and 80% methanol (PPD 3.4 g) |
|
|
TBE-300A multilayer coil planet centrifuge for performing standard HSCCC (Shanghai Tauto Biotechnique Company, China), equipped with three preparative coils connected in series (internal diameter of polytetrafluoroethylene tube, 1.6 mm; total volume, 260 mL) and a 20mL sample loop. |
|
|
n-hexane: ethyl acetate: ethanol: water = 1: 1: 1: 1, v/v |
|
|
1.5 mL/min, 850 rpm |
|
|
Agilent 1100 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), equipped with a G1311A quatPump, a sample injector with a 20 mL injection loop, a G1314A UV detector and an Agilent temperature control module. Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18-column (150 mm 4.6 mm, i.d. 5 mm), 30°C. Mobile phase is methanol: water: acetic acid = 55: 44.55: 0.45, v/v/v, 1 mL/min, UV λ280 nm |
|
|
METHOD 2 |
|
|
Fresh plant materials cut into small piece and soaked in water with Ca(OH)2 pH11 twice. Precipitate overnight, removed upper solution and passed through drum dryer to get powder. Suspended in methanol, pooled and filtered the red dye methanol solution, obtained powder after drying. Re-extracted the powder with methanol for six times. |
|
|
Introduced into silica gel 60 glass column (2.5 x 54 cm) and eluted with dichloromethane: hexane: methanol (7: 4: 0.3, v/v/v) (240 ml). The fractionated eluates were performed using RP-HPLC with ZORBAX ODS (9.4 x 250 mm) column. Mobile phase is A: 5% v/v acetonitrile, 0.1% v/v trifluoroacetic acid, B: 95% v/v acetonitrile, 0.1% v/v trifluoroacetic acid, 0-5min 20-50% B, 5-30min 50-100% B, 2mL/min, UV λ552 nm |
|
|
| Reference |
|
[1]
|
Surowiec, I., et al. (2012). "Mass spectrometric identification of new minor indigoids in shellfish purple dye from Hexaplex trunculus." Dyes and Pigments 94(2): 363-369. |
|
[2]
|
Rivest, P., et al. (2011). "Proliferative and androgenic effects of indirubin derivatives in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells at sub-apoptotic concentrations." Chemico-Biological Interactions 189(3): 177-185. |
|
[3]
|
Hsuan, S.-L., et al. (2009). "The cytotoxicity to leukemia cells and antiviral effects of Isatis indigotica extracts on pseudorabies virus." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 123(1): 61-67. |
|
[4]
|
Kim, J. H., et al. (1997). "Effect of chitosan on indirubin production from suspension culture of Polygonum tinctorium." Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering 83(2): 206-208. |
|
[5]
|
Maugard, T., et al. (2001). "Identification of an indigo precursor from leaves of Isatis tinctoria (Woad)." Phytochemistry 58(6): 897-904. |
|
[6]
|
Aobchey, P., et al. Simple Purification of Indirubin from Indigofera tinctoria Linn. and Inhibitory Effect on MCF7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. |
|
[7]
|
Lu, H. T., et al. (2012). "Preparative isolation and purification of indigo and indirubin from Folium isatidis by high-speed counter-current chromatography." Phytochem Anal 23(6): 637-641. |
|
[8]
|
Hsieh, C.-H., et al. (2006). "The kinase inhibitor indirubin-3′-oxime prevents germinal vesicle breakdown and reduces parthenogenetic development of pig oocytes." Theriogenology 65(4): 744-756. |
|
[9]
|
Mak, N.-K., et al. (2004). "Inhibition of RANTES expression by indirubin in influenza virus-infected human bronchial epithelial cells." Biochemical Pharmacology 67(1): 167-174. |
|
[10]
|
Liau, B.-C., et al. (2007). "LC-APCI-MS method for detection and analysis of tryptanthrin, indigo, and indirubin in Daqingye and Banlangen." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 43(1): 346-351. |
|
[11]
|
Oufir, M., et al. (2012). "Development and full validation of an UPLC-MS method for the determination of an anti-allergic indolinone derivative in rat plasma, and application to a preliminary pharmacokinetic study." Journal of Chromatography B 902(0): 27-34. |
|
| Link to |
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Medicinal Plant Images Database Medicinal Plant Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
|
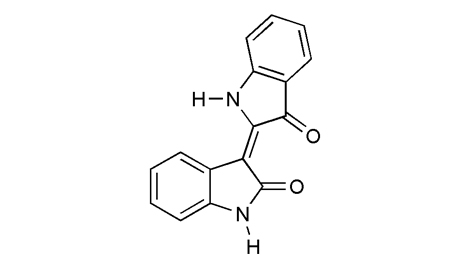
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Medicinal Plant Images Database
Medicinal Plant Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
Chinese Medicine Specimen Database


