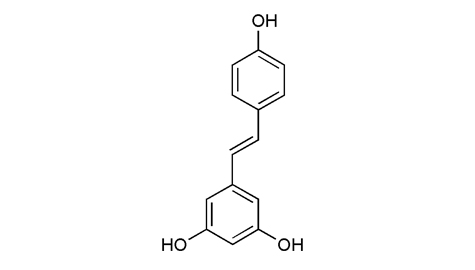
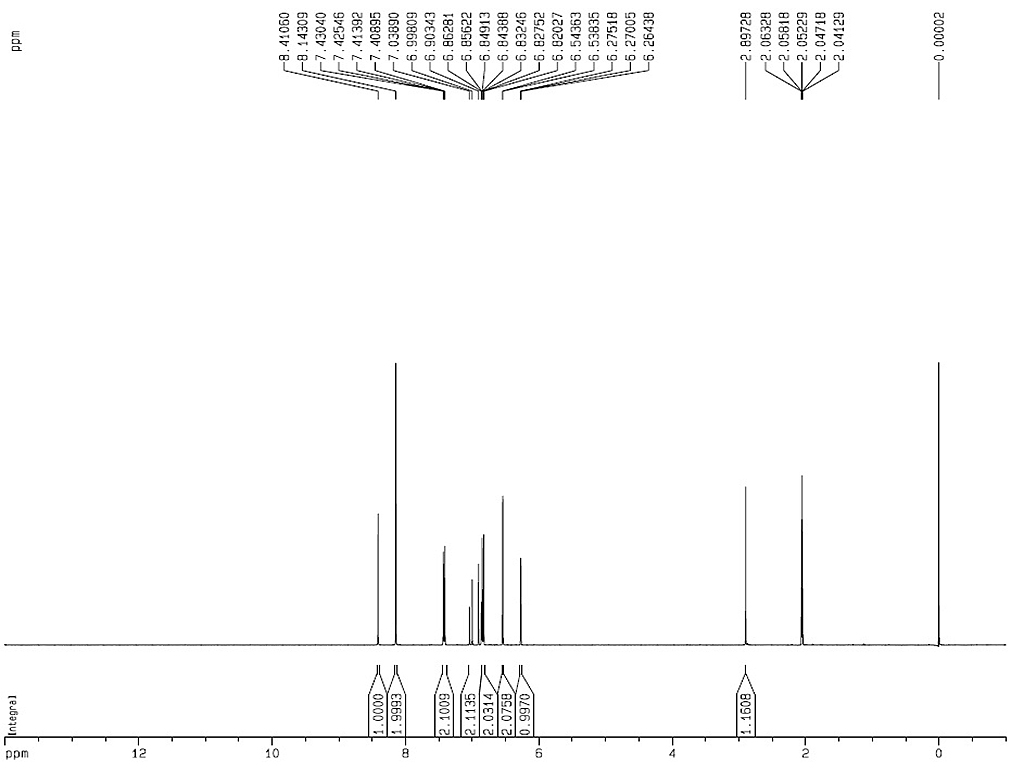
| Reference |
|
[1]
|
Ji, M., Li, Q., Ji, H., & Lou, H. (2014). "Investigation of the distribution and season regularity of resveratrol in Vitis amurensis via HPLC-DAD-MS/MS." Food Chemistry, 142(0), 61-65. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.131 |
|
[2]
|
López-Nicolás, J. M., & García-Carmona, F. (2008). "Rapid, simple and sensitive determination of the apparent formation constants of trans-resveratrol complexes with natural cyclodextrins in aqueous medium using HPLC." Food Chemistry, 109(4), 868-875. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.01.022 |
|
[3]
|
Muzzio, M., Huang, Z., Hu, S.-C., Johnson, W. D., McCormick, D. L., & Kapetanovic, I. M. (2012). "Determination of resveratrol and its sulfate and glucuronide metabolites in plasma by LC-MS and their pharmacokinetics in dogs." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 59(0), 201-208. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2011.10.023 |
|
[4]
|
Feng, Y., Wang, X.-p., Yang, S.-g., Wang, Y.-j., Zhang, X., Du, X.-t., ... Liu, R.-t. (2009). "Resveratrol inhibits beta-amyloid oligomeric cytotoxicity but does not prevent oligomer formation." NeuroToxicology, 30(6), 986-995. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2009.08.013 |
|
[5]
|
Soylemez, S., Gurdal, H., Sepici, A., & Akar, F. (2008). "The effect of long-term resveratrol treatment on relaxation to estrogen in aortae from male and female rats: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide." Vascular Pharmacology, 49(2-3), 97-105. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2008.06.006 |
|
[6]
|
Belguendouz, L., Fremont, L., & Linard, A. (1997). "Resveratrol inhibits metal ion-dependent and independent peroxidation of porcine low-density lipoproteins." Biochemical Pharmacology, 53(9), 1347-1355. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(96)00820-9 |
|
[7]
|
Notas, G., Nifli, A.-P., Kampa, M., Vercauteren, J., Kouroumalis, E., & Castanas, E. (2006). "Resveratrol exerts its antiproliferative effect on HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells, by inducing cell cycle arrest, and NOS activation." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects, 1760(11), 1657-1666. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.09.010 |
|
[8]
|
Wong, D. H., Villanueva, J. A., Cress, A. B., Sokalska, A., Ortega, I., & Duleba, A. J. (2011). "Resveratrol inhibits the mevalonate pathway and potentiates the antiproliferative effects of simvastatin in rat theca-interstitial cells." Fertility and Sterility, 96(5), 1252-1258. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.08.010 |
|
[9]
|
Chen, L., Han, Y., Yang, F., & Zhang, T. (2001). "High-speed counter-current chromatography separation and purification of resveratrol and piceid from Polygonum cuspidatum." Journal of Chromatography A, 907(1-2), 343-346. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00960-2 |
|
[10]
|
Chen, H., Tuck, T., Ji, X., Zhou, X., Kelly, G., Cuerrier, A., & Zhang, J. (2013). "Quality Assessment of Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica) Grown on Prince Edward Island as a Source of Resveratrol." J. Agric. Food Chem., 61(26), 6383-6392. doi: 10.1021/jf4019239 |
|
[11]
|
Glavnik, V., Simonovska, B., Albreht, A., & Vovk, I. (2012). "TLC and HPLC screening of p-coumaric acid, trans-resveratrol, and pterostilbene in bacterial cultures, food supplements, and wine." J. Planar Chromatogr.--Mod. TLC, 25(3), 251-258. doi: 10.1556/JPC.25.2012.3.11 |
|