|
植物来源 |
|
|
生物活性 |
|
|
鉴定 |
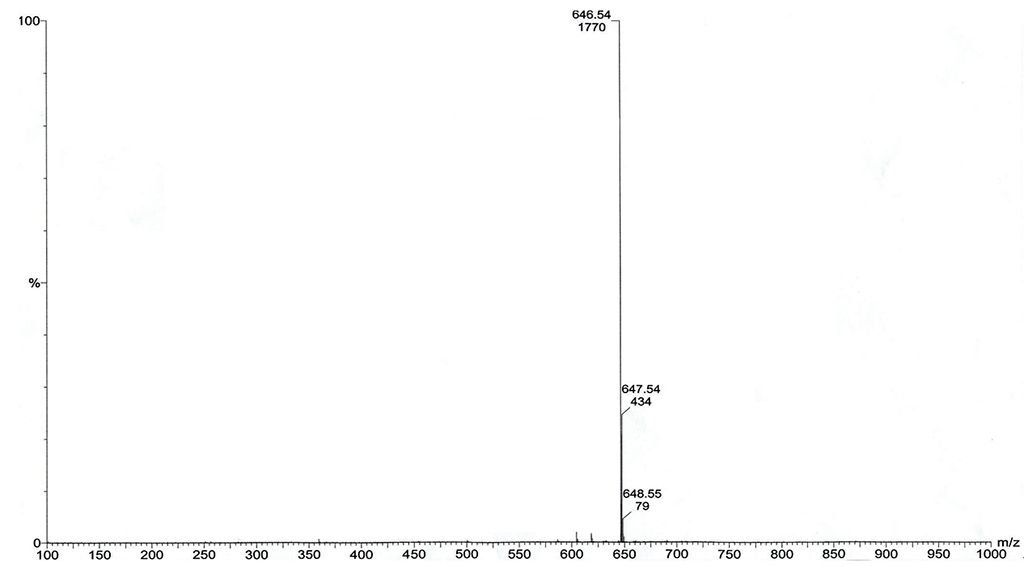
熔点 |
204°C |
| 旋亮度 |
[α]20D+19 (氯仿) |
|
|
| 分析方法 |
|
| 仪器 |
硅胶GF254 板 |
| 流动相 |
环己烷-乙酸乙酯-二乙胺 (8: 1: 1) |
| 检测器 |
Shimazu TLC model 910 反射扫描扫描 lambda s 236 nm 和 lambda R 350 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
Agilent 1100 series LC 仪器 (Hewlett-Packard, CA, USA) 包括一个G1311A 季泵, 一个G1322A 脱气器, 一个G1315A 二极管数组检测器及一个G1313A 自动进样器 |
| 色谱柱 |
Alltima™ RP18 色谱柱 (250 mm × 4.6 mm I.D.; 粒径5 µm; Alltech Associates, USA) Alltima™ RP18 保护柱 (7.5 mm × 4.6 mm I.D.), 室温 |
| 流动相 |
A: 乙腈 (ACN), B: 缓冲溶液 (包含10 mM 碳酸氢铵, 以28% 氨溶液调节pH 10.0 ± 0.2), 0-10 min, 20-25% A, 10-30 min 25-34% A, 30-67 min 34-45% A, 67-75 min 45-60% A, 1.1 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
UV λ240 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
Surveyor 液相色谱 (Thermo Finnigan Corporation, San Jose, CA, USA) 配备两个溶剂泵 |
| 色谱柱 |
Gemini C18 色谱柱 (3 µm, 150 mm × 2 mm) (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA), 包括一个 Phenomenex Luna 安全保护暗盒 C118 柱 (5 µm, 4 mm × 2.0 mm i.d.), 0-3 min 20-25% B, 3-10 min 25-28% B. |
| 流动相 |
A 相包含水和 0.005% TFA (v/v); B 相包含乙腈和 0.005% TFA (v/v). 两相都通过一个过滤器 (0.45 µm) 及脱气前处理备用, 0.1 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
VWD 1100 UV 检测器 (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany). 四极离子阱配备一个 ESI 离子源 (LCQ™, Thermo Finnigan Corporation, San Jose, CA, USA). 氦气. 正离子模式, 1.35 l/min; 4.5 kV; 175°C ; 44 V; 管透镜偏移, 0 V; 第一倍增器偏移, −5.00 V; 第二倍增器偏移, −6.50 V; 多级透镜间电压, −18.00 V. 连个碎片: IS 检测 (从 0 至 7.5 min); 三个生物碱测定 (从 7.5 至 12 min). CRM 模式选择质子化分子离子 ([M+H]+) |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
一个DX303 CG-MS 仪 (Jeol, Tokyo, Japan) 包括一个全玻璃Vandenberg-型无溶剂注射器连接一个 DA-5000 数据分析系统 (Jeol) |
| 色谱柱 |
15 m x 0.25 mm I.D. 硅胶融合毛细管交联色谱柱 5% 甲基苯硅酮 (DB-5, J&W Scientific, Folsom, CA, USA). 柱温 250°C 保持1 min, 标称调节至 320°C, 16°C/min. |
| 流动相 |
氦气, 线速度 25cm/s. 注射口和传输线温度为 320°C, 离子源 250°C. 离子化能和陷阱电流为 70eV 和 300µA. |
|
| 样品制备 |
|
方法一 |
|
|
样品粉末 (50 g) 浸于 75% 甲醇 (200 ml) 0.5 h, 75% 甲醇 (200 ml) 25°C 超生两次 30 min. 收集提取物, 35°C 浓缩至 50 ml. 13,000 rpm 离心15 min. |
|
|
| 参考文献 |
|
[1]
|
Chen, J.-H., et al. (2008). "Determination of aconitine-type alkaloids as markers in fuzi (Aconitum carmichaeli) by LC-ESI-MS3." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 48(4): 1105-1111. |
|
[2]
|
Li, M., et al. (2013). "The anti-arthritic effects of Aconitum vilmorinianum, a folk herbal medicine in Southwestern China." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 147(1): 122-127. |
|
[3]
|
Wang, Q., et al. (2013). "Naturally derived anti-inflammatory compounds from Chinese medicinal plants." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 146(1): 9-39. |
|
[4]
|
Lu, J.-y. and C. Peng (2013). "Effect of the compatibility of glycyrrhizic acid and aconitine on nerve cell." Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi 19(7): 192-195. |
|
[5]
|
Hu, H.-y. and C. Peng (2013). "Influences of compatibility of emodin and aconitine on the biomembrane of the interstitial cells of Cajal." Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi 19(7): 189-192. |
|
[6]
|
Sui, Z., et al. (2013). "Metabolite profile analysis of aconitine in rabbit stomach after oral administration by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization/multiple-stage tandem mass spectrometry." Xenobiotica 43(7): 628-635. |
|
[7]
|
Yang, C., et al. (2013). "Transcellular transport of aconitine across human intestinal Caco-2 cells." Food Chem. Toxicol. 57: 195-200. |
|
[8]
|
Voss, L. J., et al. (2008). "Aconitine induces prolonged seizure-like events in rat neocortical brain slices." European Journal of Pharmacology 584(2-3): 291-296. |
|
[9]
|
Ye, L., et al. (2013). "The role of efflux transporters on the transport of highly toxic aconitine, mesaconitine, hypaconitine, and their hydrolysates, as determined in cultured Caco-2 and transfected MDCKII cells." Toxicol Lett 216(2-3): 86-99. |
|
[10]
|
Wang K.; Tong Y.Y., 1990: "Determination of the main alkaloids in wu tou aconite by tlc densitometry." Yaoxue Xuebao. 25(5): 387-390 |
|
[11]
|
Xie, Y., et al. (2005). "Simultaneous determination of six Aconitum alkaloids in proprietary Chinese medicines by high-performance liquid chromatography." Journal of Chromatography A 1093(1-2): 195-203. |
|
[12]
|
Ito, K., et al. (1998). "Report on the preparation of deuterium-labelled aconitine and mesaconitine and their application to the analysis of these alkaloids from body fluids as internal standard." Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 714(2): 197-203. |
|
| 连结 |
 中药材图像数据库 中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库 药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库 中药标本数据库
|
 中药材图像数据库
中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库
药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库
中药标本数据库