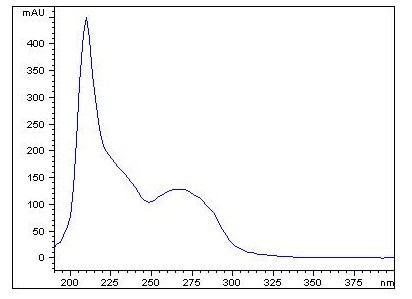
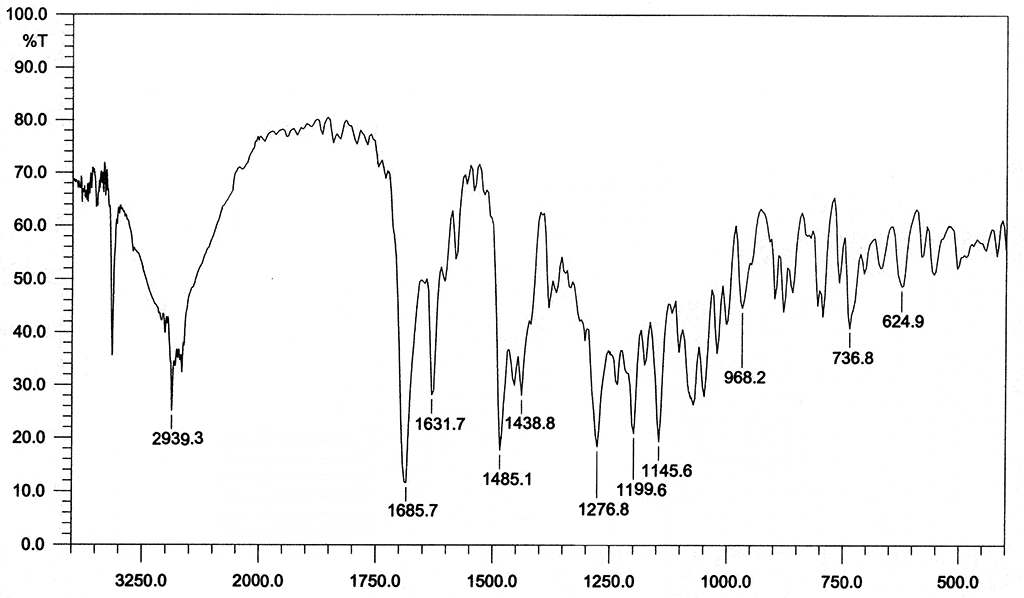
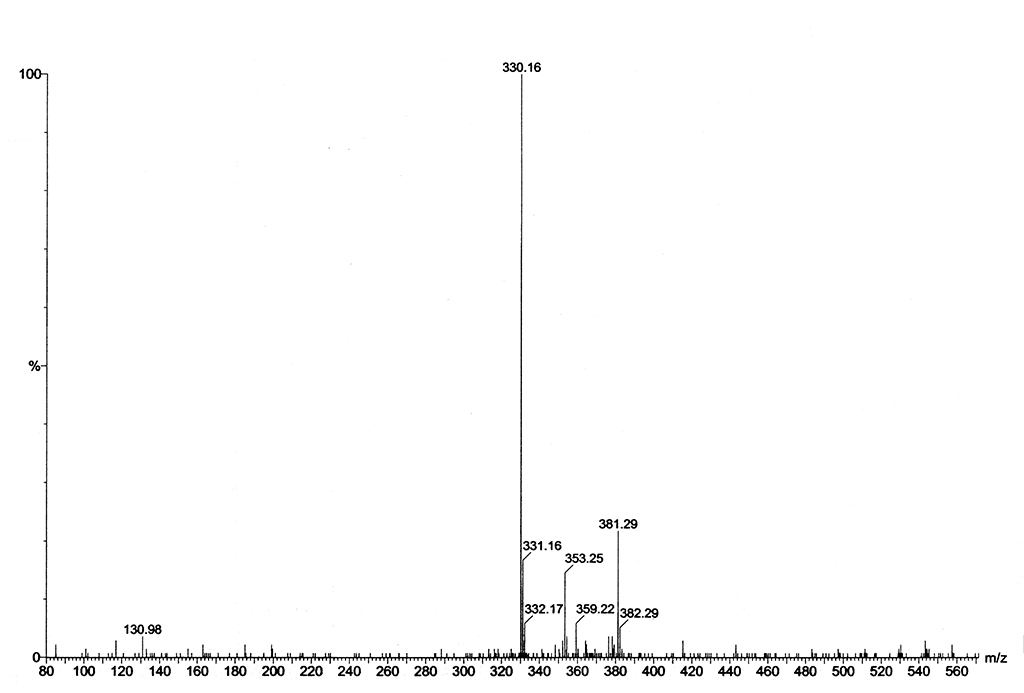
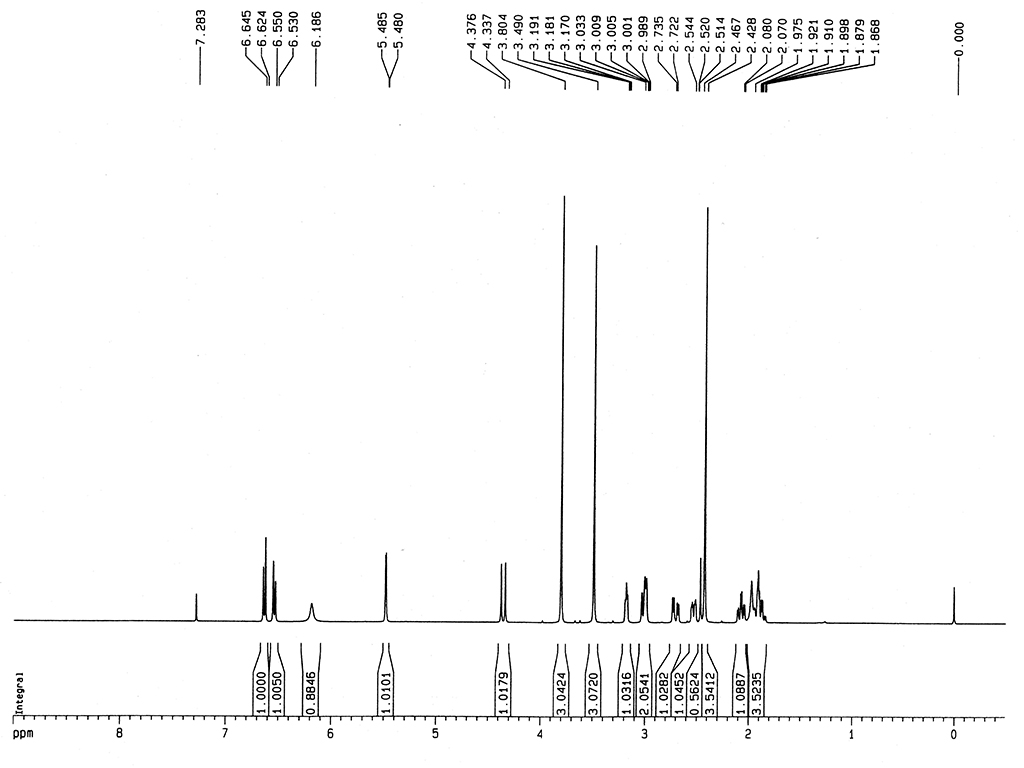
|
Natural Resources |
|
|
Bioactivities |
|
|
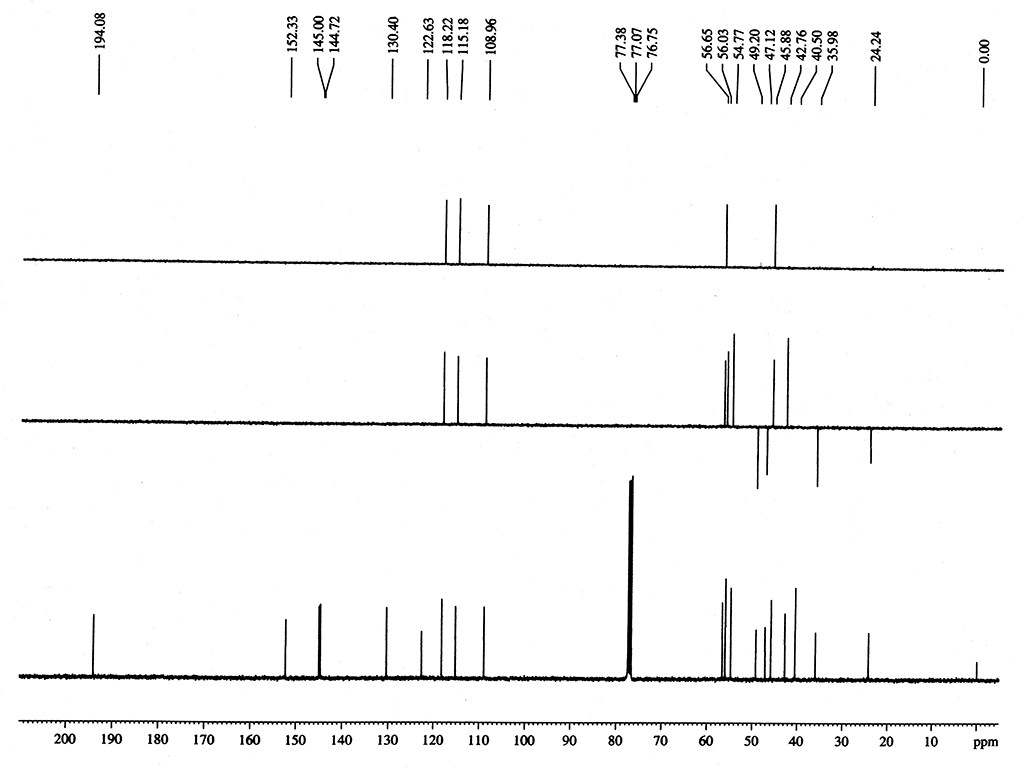
Identification |
Melting point |
161-182°C |
| Optical rotation |
[α]25D-71° (c, 2.1 in EtOH) |
|
|
| Analytical Method |
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Finnigan LCQ Deca XP™ |
| COLUMN |
Hypurity C18 column (Thermo Hypersil-Keystone 2.1 × 150 mm, 5 μm, US, 30°C) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 45% Acetonitrile, B: 55% water with 0.1% formic acid and 10 mmol/l formic; 0.2 mL/min |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent quaternary HPLC model HP 1100 series (Hewlett-Packard, Palo Alto, CA) |
| COLUMN |
Altima C18 column (250 × 4.5 mm, 5 μm, Alltech, Hong Kong) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
Aacetonitrile: 0.5% ; triethylamine water solution: 0.2% ; glacial acetic acid water solution 15 : 42.5 : 42.5, 0.45 μm Millipore filter (Millipore Hong Kong); 1 mL/min |
| DETECTION |
UV λ262 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
MPI-A system (Xi an Remax Electric Ltd. Corp., China) |
| COLUMN |
50 cm length of uncoated fused-silica capillary (25 μm i.d., Yongnian Optical Fiber Factory, Hebei, China); 15 kV |
| MOBILE PHASE |
50 mM sodium phosphate (pH 5.0), 5 mM Ru(bpy)32+ in 75 mM phosphate buffer (pH 8.0) was directly injected into the detection reservoir |
| DETECTION |
End-column ECL detection was installed with a three-electrode, 500 μm Eu-PB modifying platinum disk as a working electrode, an Ag/AgCl as a reference electrode and a platinum wire as an auxiliary electrode with sensitive photomultipier tube (PMT) was operated at 800V. |
|
| Sample Preparation |
|
METHOD 1 |
|
|
Grounded sample (2 g); the extraction vessel was preheated in the oven for 10 min; the extraction conditions : static extraction 5 min, dynamic extraction 1 hour, 40°C, 600 bar; 0.5 L/min |
|
|
Repeat: 60°C, 300 bar, carbon dioxide: 0.5 L/min gaseous fluid; methanol: 0.4 mL/min; the solution was further diluted 10 times |
|
|
| Reference |
|
[1]
|
Yi, L., et al. (2012). "Tissue-specific metabolite profiling of alkaloids in Sinomenii Caulis using laser microdissection and liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time of flight-mass spectrometry." Journal of Chromatography A 1248(0): 93-103. |
|
[2]
|
Zhao, Y., et al. (2007). "Sinomenine inhibits maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells through blocking activation of NF-kappa B." Int Immunopharmacol 7(5): 637-645. |
|
[3]
|
Yuan, Z., et al. "Dynamic pH junction high-speed counter-current chromatography coupled with EXTRACTION for online separation and purification of alkaloids from Stephania cepharantha." Journal of Chromatography A (0). |
|
[4]
|
Tsai, T.-H. and J.-W. Wu (2003). "Regulation of hepatobiliary excretion of sinomenine by P-glycoprotein in Sprague-Dawley rats." Life Sciences 72(21): 2413-2426. |
|
[5]
|
Wang, M. H., et al. (2008). "Activation of opioid μ-receptor by sinomenine in cell and mice." Neuroscience Letters 443(3): 209-212. |
|
[6]
|
Wang, C., et al. (2012). "Effect of sinomenine on IL-8 expression in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts." Di-San Junyi Daxue Xuebao 34(19): 1972-1976. |
|
[7]
|
Xiong, L. and L. Yang (2012). "Effects of alkaloid sinomenine on levels of IFN-γ, IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in a rat renal allograft model." Immunotherapy 4(8): 785-791. |
|
[8]
|
Yang, G., et al. (2011). "Sinomenine inhibits proliferation of A549 human lung cancer cells." Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Waike Zazhi 17(5): 482-485. |
|
[9]
|
Yao, Y.-M., et al. (2005). "Determination of sinomenine in human plasma by HPLC/ESI/ion trap mass spectrum." Clinica Chimica Acta 356(1-2): 212-217. |
|
[10]
|
Liu, Z.-Q., et al. (2005). "The pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of sinomenine in rats and its protein binding ability in vitro." Life Sciences 77(25): 3197-3209. |
|
[11]
|
Zhou, M., et al. (2007). "Determination of sinomenine in Sinomenium acutum by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemiluminescence detection." Analytica Chimica Acta 587(1): 104-109. |
|
[12]
|
Liu, B., et al. (2005). "Supercritical fluid extraction of sinomenine from Sinomenium acutum (Thumb) Rehd et Wils." Journal of Chromatography A 1075(1-2): 213-215. |
|
| Link to |
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
|
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
Chinese Medicine Specimen Database