|
Natural Resources |
|
|
Bioactivities |
|
|
Identification |
Optical rotation |
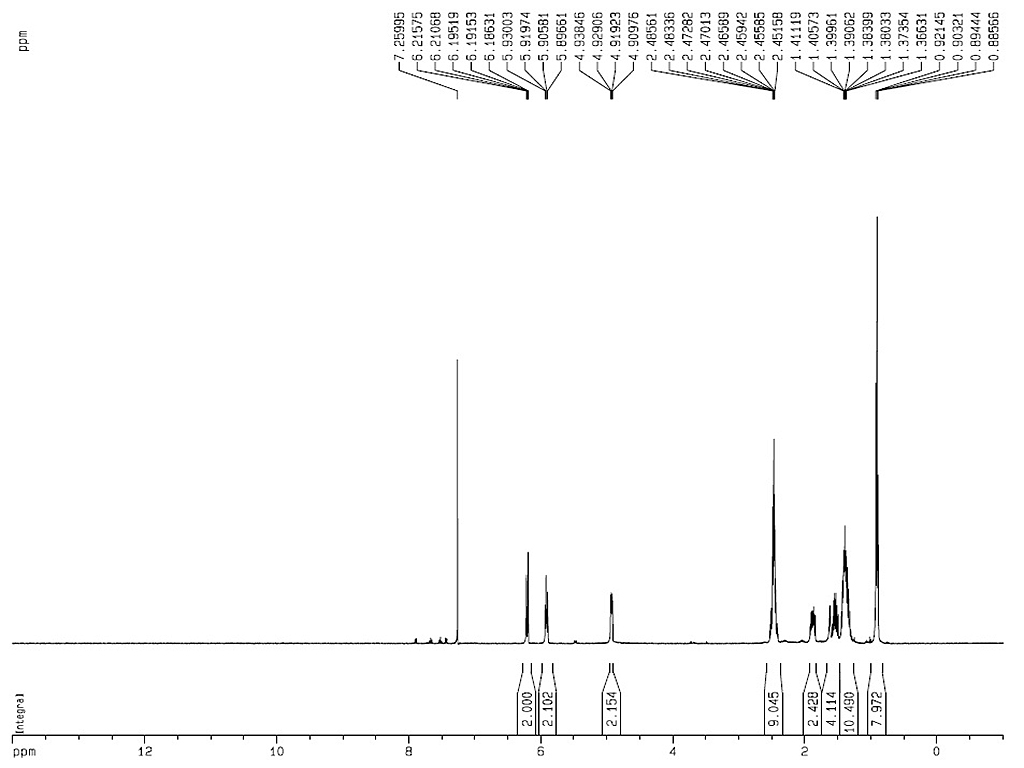
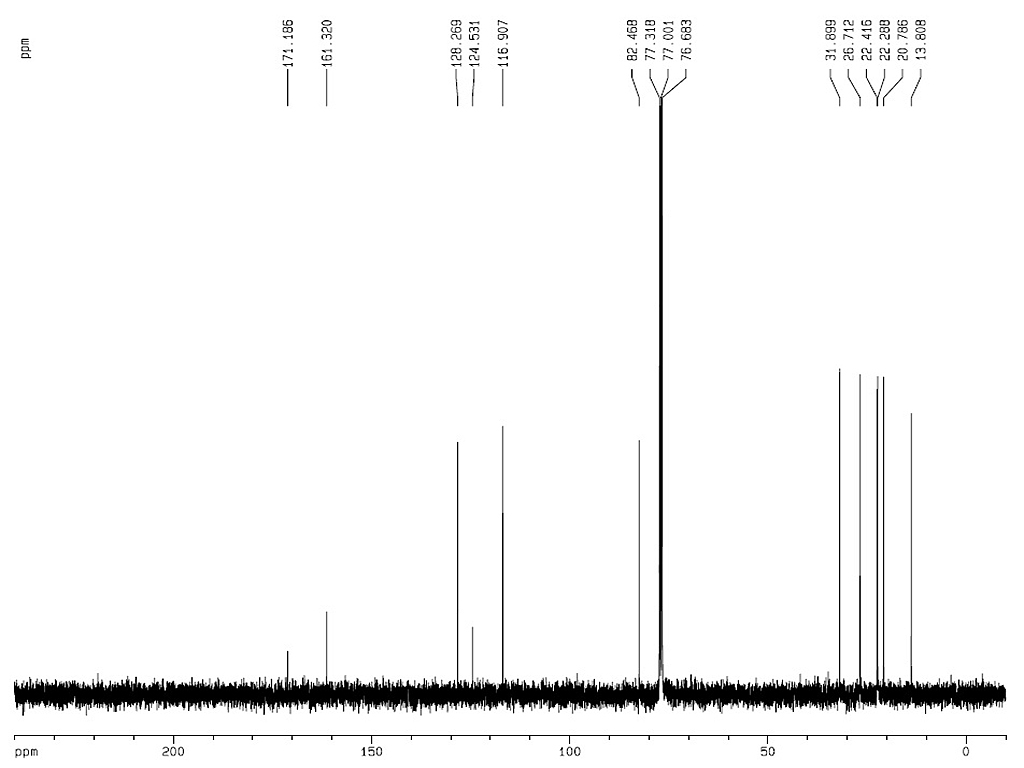
[α]18D-60.5 (c, 0.5 in chloroform)
[α]24D-43.2 (EtOH) |
|
|
| Analytical Method |
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Silica gel 60 F254 preparative TLC plates (1.0 mm thickness, 20 x 20 cm, E. Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
Petroleum: ether-ethyl acetate = 85 : 15, v/v |
| DETECTION |
UV λ280 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1290 UPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany), and Aglient 6520 Q-TOF mass spectrometer (Agilent Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was connected to the Agilent 1290 UPLC via an ESI interface. The quantitative analysis was carried out on a Waters Acquity UPLC™ instrument (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) equipped with DAD. |
| COLUMN |
ZORBAX SB-C18 column (100 mm × 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm particle size, Agilent), 50°C |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 0.1% formic acid-water, B: acetonitrile, 0-7 min 5-17% B, 7-14 min 17-25% B, 14-16 min 25-28% B, 16-22 min 28-30% B, 22-33 min 30-85% B, 33-40 min 85-95% B, 0.4 mL/min. |
| DETECTION |
Positive and negative ion modes, drying gas (N2): 10.0 L/min 350°C, nebulizer gas: 40 psig, capillary: 4500 V, fragmentor: 150 V, skimmer: 65 V, octopole RF: 750 V |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1290 UPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany), and Aglient 6520 Q-TOF mass spectrometer (Agilent Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was connected to the Agilent 1290 UPLC via an ESI interface. The quantitative analysis was carried out on a Waters Acquity UPLC™ instrument (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) equipped with DAD. |
| COLUMN |
ZORBAX SB-C18 column (100 mm × 4.6 mm, 1.8 μm particle size, Agilent), 50°C |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 0.1% formic acid-water, B: acetonitrile, 0-7 min 5-17% B, 7-14 min 17-25% B, 14-16 min 25-28% B, 16-22 min 28-30% B, 22-33 min 30-85% B, 33-40 min 85-95% B, 0.4 mL/min. |
| DETECTION |
UV λ230 nm, UV λ250 nm, UV λ280 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Shimadzu LC-20AVP system equipped with two LC-20AT solvent delivery units, an SPD-M20AVP UV-vis photodiode array detector (DAD) system, a Model 7725 injection valve with a 20 μL loop and an auto-sampler, an SCL-20AVP system controller, and a Class-VP-LC work station (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). |
| COLUMN |
Apollo C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm I.D., 5 μm), 30°C |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: MeOH, B: 0.05% H3PO4, 0-3 min 45-40% B, 3-17 min 40-33% m, 17-43 min 33%, 1 mL min |
| DETECTION |
UV λ254 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1100 series HPLC-DAD system comprising a vacuum degasser, binary pump, autosampler, thermostated column compartment, and DAD (Hewlett Packard, U.S.A.) was used for quantitative analysis and UV spectra acquisition. |
| COLUMN |
Alltima C18 column (5μm, 4.6mm × 150 mm, Alltech Associates, Inc., U.S.A.) with a compatible guard column (C18, 5μm, 4.6mm × 7.5 mm), 30°C |
| MOBILE PHASE |
1% acetic acid in water : methanol = 40 : 60, 1 mL/min |
| DETECTION |
UV λ280 nm. Applied Biosystems/PESCIEX API 365 LC-MS system with electrospray ionization source (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, U.S.A.). drying gas: 7 L/min 300°C, scan range: 50-500 u, orifice: 26V, focusing: 170V, and electrospray: 5000V. |
|
| Sample Preparation |
|
METHOD 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
HSCCC instrument (Beijing Institute of New Technology Application, Beijing, China) used was a Model GS-20 A analytical multilayer coil planet centrifuge equipped with a PTFE multilayer coil of 70 m × 0.85 mm I.D. with a total capacity of 40 mL |
|
|
n: hexane: ethyl acetate: methanol: water: acetonitrile = 8: 2: 5: 5: 5, v/v |
|
|
1.0 mL/min, 1600 rpm |
|
|
UV λ254 nm |
|
|
METHOD 2 |
|
|
Sample powder was macerated in 95% ethanol at room temperature with continous sonication for 30 min. And solvent partitions sequentially with n-C6H14 EtOAc and n-BuOH. |
|
|
EtOAc fraction was applied to silica gel column and eluted by 100% EtOAc, EtOAc and CH3OH (8: 2), EtOAc and CH3OH (1: 2), CH3OH 100%. The pure senkyunolide A was obtained from the eluate of EtOAc 100% fractions. |
|
|
| Reference |
|
[1]
|
Or, T. C. T., et al. (2011). "Isolation and identification of anti-inflammatory constituents from Ligusticum chuanxiong and their underlying mechanisms of action on microglia." Neuropharmacology 60(6): 823-831. |
|
[2]
|
Liu, L., et al. (2005). "Phthalide lactones from Ligusticum chuanxiong inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α production and TNF-α-mediated NF-κB activation." Planta Med. 71(9): 808-813. |
|
[3]
|
Chan, S. S.-K., et al. (2007). "Relaxation effects of ligustilide and senkyunolide A, two main constituents of Ligusticum chuanxiong, in rat isolated aorta." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 111(3): 677-680. |
|
[4]
|
Yi, T., et al. (2005). "Identification and comparative determination of senkyunolide A in traditional chinese medicinal plants Ligusticum chuanxiong and Angelica sinensis by HPLC coupled with DAD and ESI-MS." Chem. Pharm. Bull. 53(11): 1480-1483. |
|
[5]
|
Dong, J., et al. (2013). "Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the major constituents in Chinese medicinal preparation Dan-Lou tablet by ultra high performance liquid chromatography/diode-array detector/quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 80(0): 50-62. |
|
[6]
|
Wei, Y., et al. (2013). "Online isolation and purification of four phthalide compounds from Chuanxiong rhizoma using high-speed counter-current chromatography coupled with semi-preparative liquid chromatography." Journal of Chromatography A 1284(0): 53-58. |
|
| Link to |
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Medicinal Plant Images Database Medicinal Plant Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
|
 Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
Chinese Medicinal Material Images Database
 Medicinal Plant Images Database
Medicinal Plant Images Database
 Chinese Medicine Specimen Database
Chinese Medicine Specimen Database