|
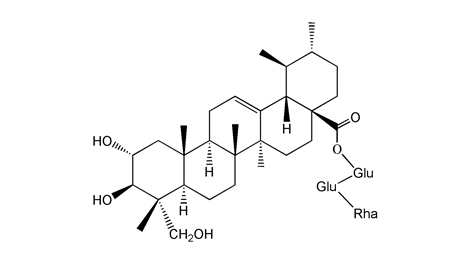
植物來源 |
|
|
生物活性 |
|
|
鑑定 |
熔點 |
235-238° |
| 旋光度 |
[α]20D-14° (EtOH) |
1HNMR

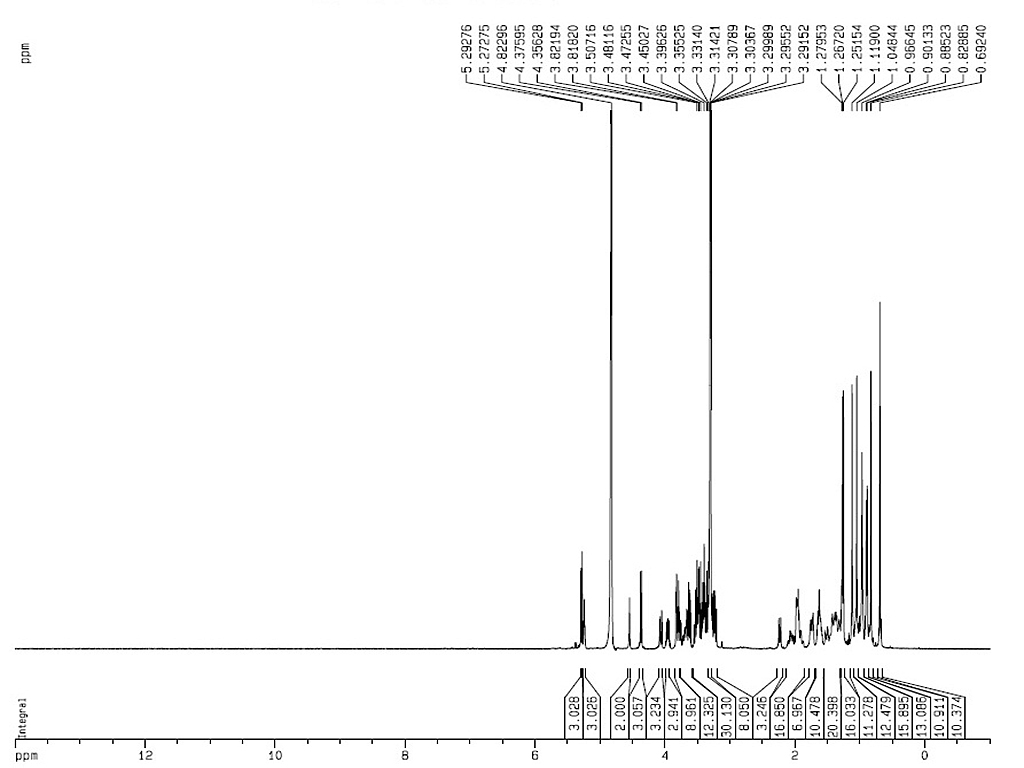
|
| 分析方法 |
|
| 儀器 |
10 × 10 cm 矽膠60 F254-塗板, 集中區10 × 2.5 cm (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) 無熒光顯色劑 |
| 流動相 |
乙酸乙酯: 甲醇 = 60: 40, v/v |
| 檢測器 |
茴香醛溶液噴淋, 加熱 100-105°C 日光下顯色 |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
Model Nanospace SI-2/3201 泵, 3002 UV 檢測器 |
| 色譜柱 |
Kinetex C18 色譜柱 (100 × 2.1 mm I.D., 2.6 µm, Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) |
| 流動相 |
25% v/v 乙腈 |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ203 nm |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
Agilent 1100儀 |
| 色譜柱 |
Eclipse XDB-C18 反相色譜柱 (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 µm, Agilent) |
| 流動相 |
甲醇: 乙腈: 乙酸: 0.3% : 水 = 41: 11: 2: 46, v/v/v/v |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ225 nm |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
Shisheido HPLC 儀 (NANOSPACE, Shisheido, Tokyo, Japan), SI-1/2001 泵, 自動六埠切換閥 (SI-2012), 自動進樣器 (SI-1/2003) 配備脫氣機 (SI-1/2009) 及UV-Vis 檢測器 (SI-1/2002) |
| 色譜柱 |
Capcell Pak C18 UG120柱 (250 × 1.5 mm, 5 µm, Shisheido) |
| 流動相 |
A: 10 mM 磷酸鈉 (pH 6.86), B: 50% 乙腈/去離子水 (v/v) |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ210 nm |
|
| 樣品製備 |
|
方法一 |
|
|
2000 mL 乙醇-水 (70: 30, v/v) 提取. 膜過濾純化幷蒸幹。加入純水得羥基積雪草苷和積雪草苷溶液。 |
|
|
玻璃柱開展動態吸附和解吸 (12 mm × 50 mm) 濕式填料水和 HPD100 樹脂. 8 mL 樹脂. 用蒸餾水 4 BV 沖洗柱, 乙醇-水洗脫 (40: 60, v/v) 至飽和溶液, 各溶液1 BV. HPLC 分析得積雪草苷. 濃縮幷真空乾燥. |
|
|
| 參考文獻 |
|
[1]
|
Kwon, H.-J., et al. (2011). "Determination of madecassoside and asiaticoside contents of C. asiatica leaf and C. asiatica-containing ointment and dentifrice by HPLC-coupled pulsed amperometric detection." Microchemical Journal 98(1): 115-120. |
|
[2]
|
Lin, X., et al. (2013). "Beneficial effects of asiaticoside on cognitive deficits in senescence-accelerated mice." Fitoterapia 87(0): 69-77. |
|
[3]
|
Paolino, D., et al. (2012). "Improved in vitro and in vivo collagen biosynthesis by asiaticoside-loaded ultradeformable vesicles." Journal of Controlled Release 162(1): 143-151. |
|
[4]
|
Shukla, A., et al. (1999). "In vitro and in vivo wound healing activity of asiaticoside isolated from Centella asiatica." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 65(1): 1-11. |
|
[5]
|
Xu, C.-L., et al. (2012). "Asiaticoside: Attenuation of neurotoxicity induced by MPTP in a rat model of Parkinsonism via maintaining redox balance and up-regulating the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 100(3): 413-418. |
|
[6]
|
Liang, X., et al. (2008). "Antidepressant-like effect of asiaticoside in mice." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 89(3): 444-449. |
|
[7]
|
Chen, S. W., et al. (2006). "Anxiolytic-like effect of asiaticoside in mice." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 85(2): 339-344. |
|
[8]
|
Zhang, L., et al. (2010). "Protective effects of Asiaticoside on acute liver injury induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine in mice." Phytomedicine 17(10): 811-819. |
|
[9]
|
Bonfill, M., et al. (2005). "Identification of triterpenoid compounds of Centella asiatica by thin-layer chromatography and mass spectrometry." |
|
[10]
|
Jia, G. and X. Lu (2008). "Enrichment and purification of madecassoside and asiaticoside from Centella asiatica extracts with macroporous resins." Journal of Chromatography A 1193(1–2): 136-141. |
|
[11]
|
Baek, M., et al. (1999). "Column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for determination of asiaticoside in rat plasma and bile with ultraviolet absorbance detection." Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 732(2): 357-363. |
|
[12]
|
Jia, G. and X. Lu (2008). "Enrichment and purification of madecassoside and asiaticoside from Centella asiatica extracts with macroporous resins." Journal of Chromatography A 1193(1–2): 136-141. |
|
| 連結 |
 藥用植物圖像數據庫 藥用植物圖像數據庫
|
 藥用植物圖像數據庫
藥用植物圖像數據庫


