|
Natural Resources |
|
|
Bioactivities |
|
|
Identification |
Melting point |
235-238° |
| Optical rotation |
[α]20D-14° (EtOH) |
1HNMR

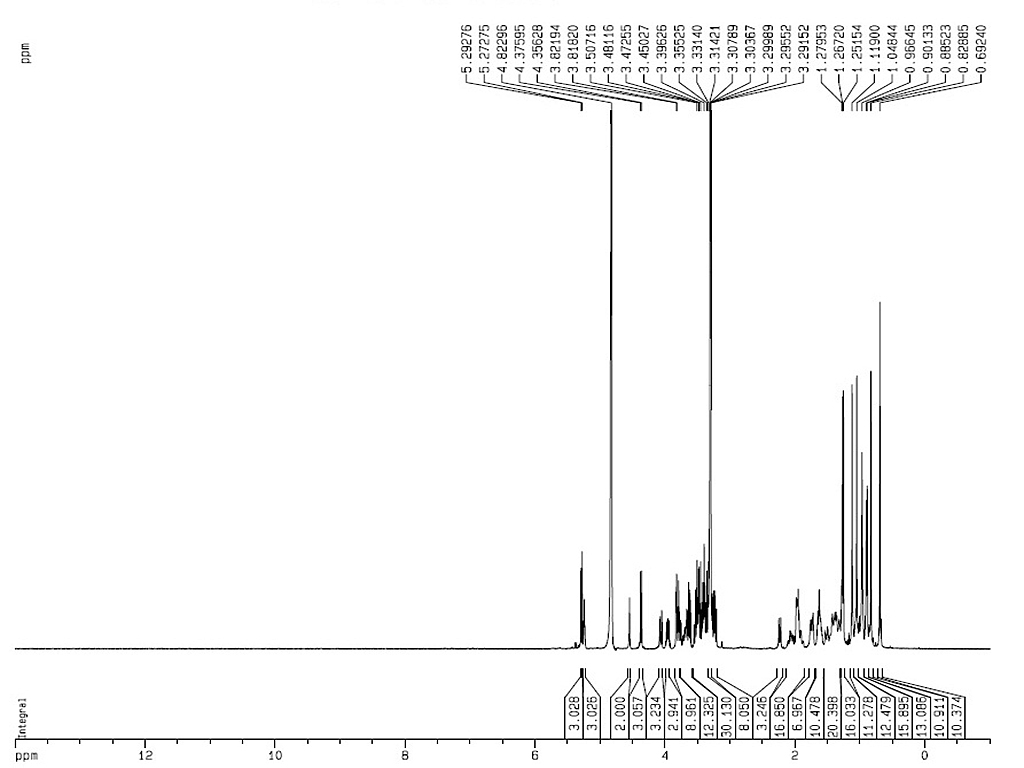
|
| Analytical Method |
|
| INSTRUMENT |
10 × 10 cm silica gel 60 F254-covered plates with concentrating zone of 10 × 2.5 cm (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) without a fluorescent indicator |
| MOBILE PHASE |
Ethyl acetate: methanol = 60: 40, v/v |
| DETECTION |
Spray with anisaldehyde solution, heated at 100-105°C and visualize under daylight. |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Model Nanospace SI-2/3201 pump, 3002 UV detector |
| COLUMN |
Kinetex C18 column (100 × 2.1 mm I.D., 2.6 µm, Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
25% v/v acetonitrile |
| DETECTION |
UV λ203 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Agilent 1100 |
| COLUMN |
Eclipse XDB-C18 reversed-phase column (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 µm, Agilent) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
Methanol: acetonitrile: acetic acid: 0.3% : water = 41: 11: 2: 46, v/v/v/v |
| DETECTION |
UV λ225 nm |
|
|
|
| INSTRUMENT |
Shisheido HPLC system (NANOSPACE, Shisheido, Tokyo, Japan) with SI-1/2001 pump, an automatic six-port switching valve (SI-2012), an autosampler (SI-1/2003) coupled to the degasser (SI-1/2009) and UV-Vis detector (SI-1/2002) |
| COLUMN |
Capcell Pak C18 UG120 (250 × 1.5 mm, 5 µm, Shisheido) |
| MOBILE PHASE |
A: 10 mM sodium phosphate (pH 6.86), B: 50% acetonitrile in deionized water (v/v) |
| DETECTION |
UV λ210 nm |
|
| Sample Preparation |
|
METHOD 1 |
|
|
Extract Centella asiatica by 2000 mL of ethanol-water (70: 30, v/v) solution. Purify the extracts by membrane filtration and evaporate it to dryness. Add distilled water to get madecassoside and asiaticoside solutions. |
|
|
Carry out dynamic adsorption and desorption on glass columns (12 mm × 50 mm) wet-packed with hydrated HPD100 resin. The bed volume (BV) of resin is 8 mL. Wash the column by distilled water with 4 BV, then elute it by ethanol-water (40: 60, v/v) solution after reaching adsorptive saturation, and the volume of each solution was 1 BV. Analyze each desorption solutions by HPLC to obtain asiaticoside. Concentrate the solution to dryness under vacuum. |
|
|
| Reference |
|
[1]
|
Kwon, H.-J., et al. (2011). "Determination of madecassoside and asiaticoside contents of C. asiatica leaf and C. asiatica-containing ointment and dentifrice by HPLC-coupled pulsed amperometric detection." Microchemical Journal 98(1): 115-120. |
|
[2]
|
Lin, X., et al. (2013). "Beneficial effects of asiaticoside on cognitive deficits in senescence-accelerated mice." Fitoterapia 87(0): 69-77. |
|
[3]
|
Paolino, D., et al. (2012). "Improved in vitro and in vivo collagen biosynthesis by asiaticoside-loaded ultradeformable vesicles." Journal of Controlled Release 162(1): 143-151. |
|
[4]
|
Shukla, A., et al. (1999). "In vitro and in vivo wound healing activity of asiaticoside isolated from Centella asiatica." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 65(1): 1-11. |
|
[5]
|
Xu, C.-L., et al. (2012). "Asiaticoside: Attenuation of neurotoxicity induced by MPTP in a rat model of Parkinsonism via maintaining redox balance and up-regulating the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 100(3): 413-418. |
|
[6]
|
Liang, X., et al. (2008). "Antidepressant-like effect of asiaticoside in mice." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 89(3): 444-449. |
|
[7]
|
Chen, S. W., et al. (2006). "Anxiolytic-like effect of asiaticoside in mice." Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 85(2): 339-344. |
|
[8]
|
Zhang, L., et al. (2010). "Protective effects of Asiaticoside on acute liver injury induced by lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine in mice." Phytomedicine 17(10): 811-819. |
|
[9]
|
Bonfill, M., et al. (2005). "Identification of triterpenoid compounds of Centella asiatica by thin-layer chromatography and mass spectrometry." |
|
[10]
|
Jia, G. and X. Lu (2008). "Enrichment and purification of madecassoside and asiaticoside from Centella asiatica extracts with macroporous resins." Journal of Chromatography A 1193(1–2): 136-141. |
|
[11]
|
Baek, M., et al. (1999). "Column-switching high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for determination of asiaticoside in rat plasma and bile with ultraviolet absorbance detection." Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications 732(2): 357-363. |
|
[12]
|
Jia, G. and X. Lu (2008). "Enrichment and purification of madecassoside and asiaticoside from Centella asiatica extracts with macroporous resins." Journal of Chromatography A 1193(1–2): 136-141. |
|
| Link to |
 Medicinal Plant Images Database Medicinal Plant Images Database
|
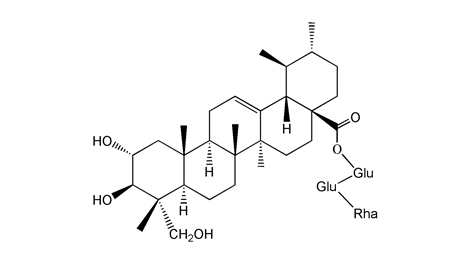
 Medicinal Plant Images Database
Medicinal Plant Images Database


