|
植物来源 |
|
|
生物活性 |
|
|
鉴定 |
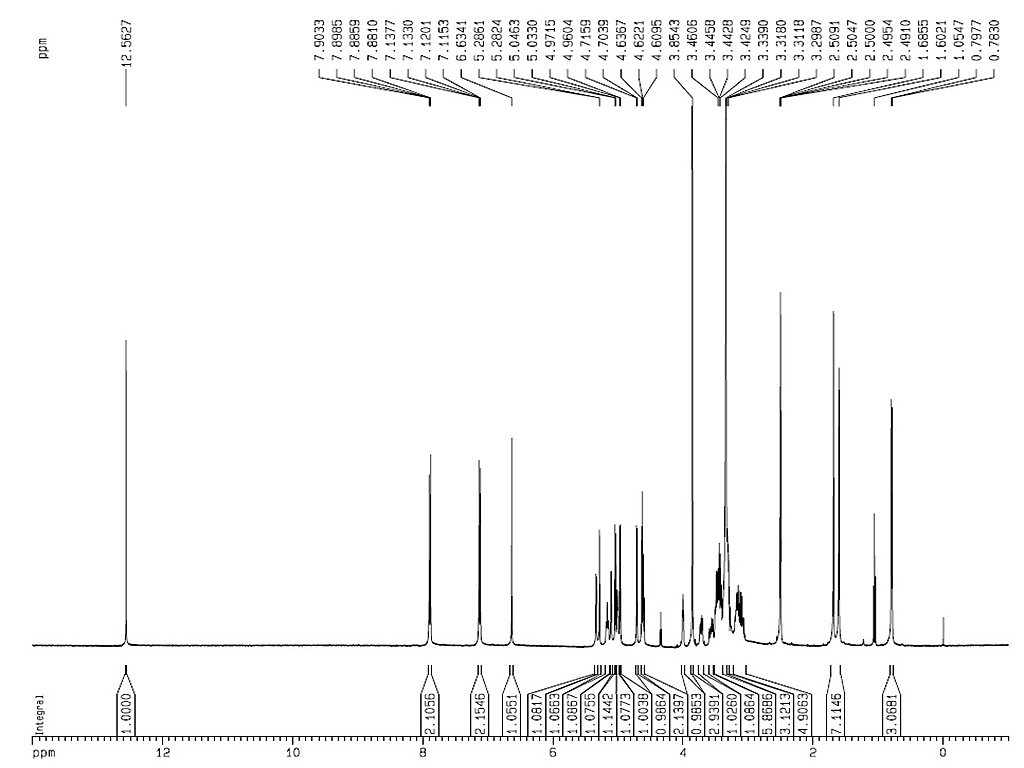
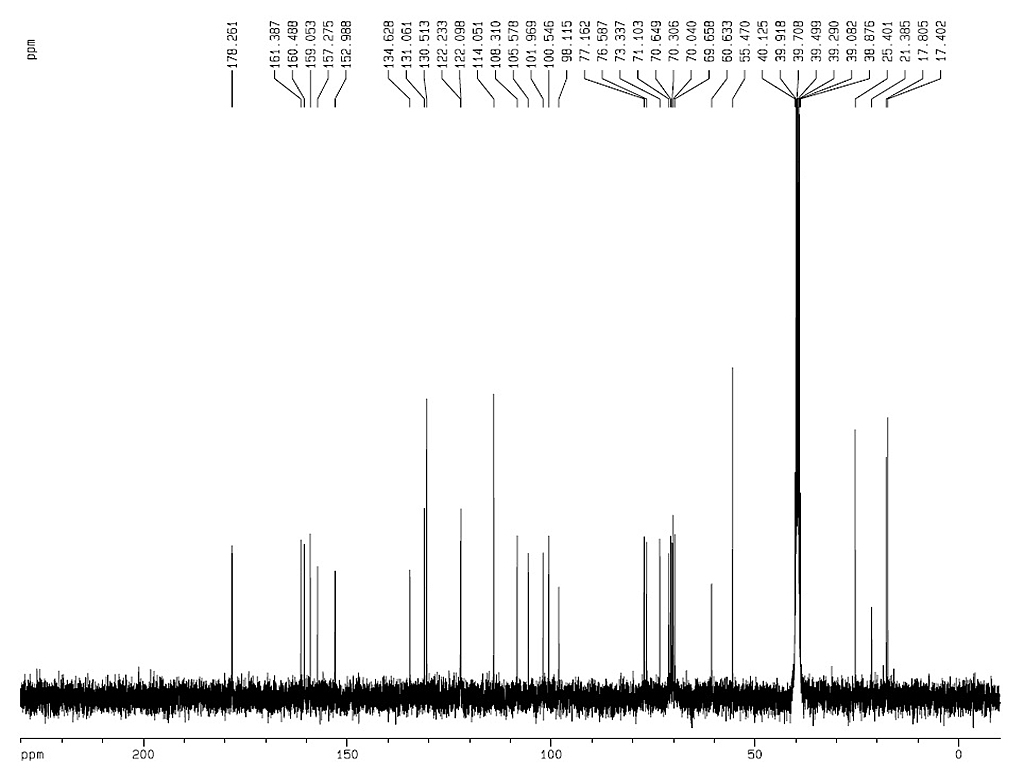
熔点 |
231-235°C (226-229°C) |
| 旋亮度 |
[α]15D-87.1° (Py) |
|
|
| 分析方法 |
|
| 仪器 |
硅胶H 板 |
| 流动相 |
氯仿: 甲醇: 甲酸 = 15: 1: 0.2, v/v |
| 检测器 |
5% 三氯化铁的乙酸喷淋显色 |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
LC-10ATVP HPLC 泵, Shimadzu, Japan |
| 色谱柱 |
ODS 色谱柱 (Shim-pack VP-ODS 4.6 mm × 150 mm, 5.0 μm, Dikma, Beijing) |
| 流动相 |
乙腈: 3% 乙酸 = 29: 71, v: v, 1.0, 1.1 和1.0 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
UV λ270 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
Waters Acquity™ 仪包括二极管数组检测器 (DAD) |
| 色谱柱 |
Acquity UPLC BEH C18 色谱柱 (50 mm × 2.1 mm i.d., 1.7 mm; Waters, Milford, MA, USA) |
| 流动相 |
A: 100% 缓冲液 = 2.5 mM NH4Ac, pH 7.4, B: 100% 乙腈, 0.45 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
UV λ254 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
The Agilent G6410A 三重四极杆串联液相色谱-质谱系统 |
| 色谱柱 |
ZORBAX SB-C18 色谱柱 (3.5 μm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm) 和 C18 保护柱 (5 μm, 4.0 mm × 2.0 mm), 35°C |
| 流动相 |
乙腈: 水: 甲酸 = 50: 50: 0.05, v/v/v, 0.25 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
正离子模式, 4000 V, 雾化气 40 psi, 10 L/min |
|
| 样品制备 |
|
方法一 |
|
|
两相溶剂系统正己烷-正丁醇-甲醇-水 (1: 4: 2: 6, v/v). 两个多层螺旋星式离心. 300 mg 提取物利用半制备仪器分离 230-ml 色谱柱分离103 mg 淫羊藿苷, 纯度 86.2%. |
|
|
8 g 提取物利用大型制备仪器分离 2460-ml 色谱柱分离 2.45 g 淫羊藿苷纯度 85.7%. 馏分中 98% 纯淫羊藿苷水中重结晶备用. |
|
|
| 参考文献 |
|
[1]
|
Yang, L., et al. (2013). "Icariin from Epimedium brevicornum Maxim promotes the biosynthesis of estrogen by aromatase (CYP19)." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 145(3): 715-721. |
|
[2]
|
Hsieh, T.-P., et al. (2010). "Icariin isolated from Epimedium pubescens regulates osteoblasts anabolism through BMP-2, SMAD4, and Cbfa1 expression." Phytomedicine 17(6): 414-423. |
|
[3]
|
Li, H.-f., et al. (2012). "Antioxidant flavonoids from Epimedium wushanense." Fitoterapia 83(1): 44-48. |
|
[4]
|
Zhang, D. W., et al. (2008). "Effects of total flavonoids and flavonol glycosides from Epimedium koreanum Nakai on the proliferation and differentiation of primary osteoblasts." Phytomedicine 15(1–2): 55-61. |
|
[5]
|
Wang, L., et al. (2009). "Icariin enhances neuronal survival after oxygen and glucose deprivation by increasing SIRT1." European Journal of Pharmacology 609(1–3): 40-44. |
|
[6]
|
Wang, F., et al. (2012). "Icariin enhances the healing of rapid palatal expansion induced root resorption in rats." Phytomedicine 19(11): 1035-1041. |
|
[7]
|
Zhu, J., et al. (2008). "TLC identification for four medicinal materials and the determination of icariin in Tianshenyizhi capsule." Shizhen Guoyi Guoyao 19(2): 324-326. |
|
[8]
|
Li, Y., et al. (2009). "In vivo pharmacokinetics comparisons of icariin, emodin and psoralen from Gan-kang granules and extracts of Herba Epimedii, Nepal dock root, Ficus hirta yahl." Journal of Ethnopharmacology 124(3): 522-529. |
|
[9]
|
Liu, W., et al. (2011). "Sensitive and robust UPLC–MS/MS method to determine the gender-dependent pharmacokinetics in rats of emodin and its glucuronide." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 54(5): 1157-1162. |
|
[10]
|
Xu, W., et al. (2007). "LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of icariin and its major metabolites in rat plasma." Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 45(4): 667-672. |
|
[11]
|
Du, Q., et al. (2002). "Purification of icariin from the extract of Epimedium segittatum using high-speed counter-current chromatography." Journal of Chromatography A 962(1–2): 239-241. |
|
| 连结 |
 中药材图像数据库 中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库 药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库 中药标本数据库
|
 中药材图像数据库
中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库
药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库
中药标本数据库