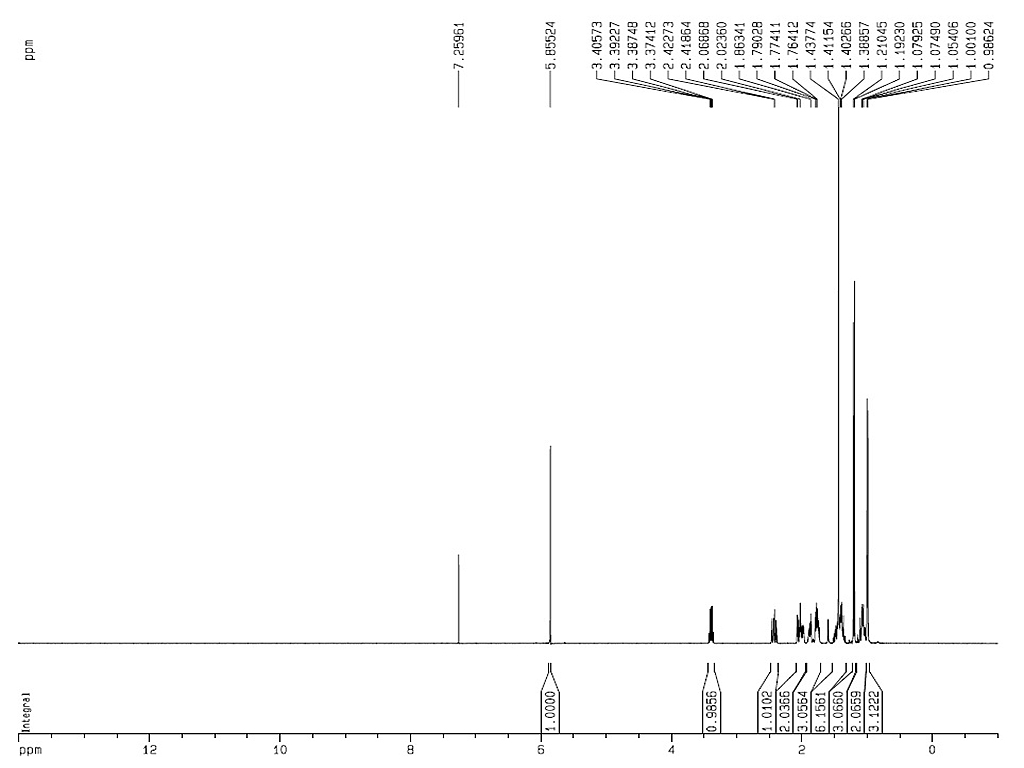
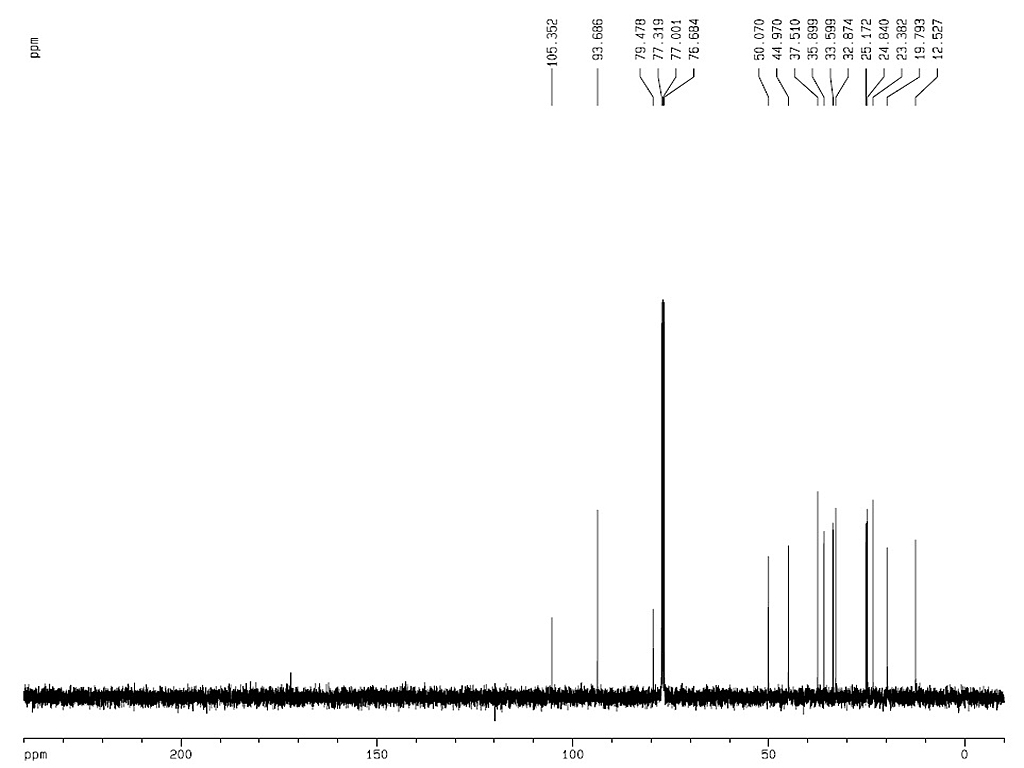
|
植物来源 |
|
|
生物活性 |
|
|
鉴定 |
熔点 |
152-157°C |
| 旋亮度 |
[α]20D+64 to +66° (C=2.0g/100ml, 氯仿) |
|
|
| 分析方法 |
|
| 仪器 |
RP-C18 薄层板 |
| 流动相 |
氯仿: 甲醇 = 60: 10 v/v |
| 检测器 |
UV λ215 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
Varian Prostar 仪器配置一个可变波长UV检测器, 自动进样器, 和柱恒温器, Varian MS 工作站Ver. 6.8 (Varian Associates, Palo Alto, CA, USA) 操作及收集资料 |
| 色谱柱 |
C-18 色谱柱 (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) (LUNA Phenomenex, USA) |
| 流动相 |
乙腈: 0.1% 乙酸 = 60: 40, 1.0 mL /min |
| 检测器 |
UV λ254 nm |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
Hitachi (Hitachi Technologies, Atlanta, GA) L-7100 梯度季泵配置一个脱气机, L-7250 可程序设计自动采样器, PL-ELS1000 ELSD 检测器 (Polymer Laboratories, Amherst, MA), Hitachi D-7000 HPLC System Manager 软件收集数据. |
| 色谱柱 |
Endcapped Purosphere (Hitachi Technologies, Atlanta, GA) C18-RP 色谱柱 250 mm × 4.0 mm ID (5.0 × m) |
| 流动相 |
A: 等渡和水, pH 3.0-3.5, 三氯乙酸 (TFA), B: 乙腈 (65: 35), 1.0 mL/min |
| 检测器 |
ELSD 参数: 蒸发温度 80°C, 雾化温度 75°C, 氮气 0.8 L/min |
|
|
|
| 仪器 |
GC-2010 仪 (Shimadzu, Columbia, MD) 配置一个火焰电离检测器及Shimadzu GC-Solution 软件用于收集数据. |
| 色谱柱 |
Rtx-5 跨接联轨线跨接联轨线跨接联轨线用连接线 100% 二甲基聚硅氧烷 (Resteck Corp), (15 m × 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 × m film thickness). 柱温195°C, 进样器 240°C, FID 温度300°C, 进样速率 40 ms. |
| 流动相 |
载气氦气: 压力: 15.6 psi, 总流量: 37.4 mL/min, 柱流量: 1.50 mL/min, 线速度: 50.5 cm/s, 清楚流量: 3.0 mL/min, 分流比 21: 9 |
| 检测器 |
FID 温度: 300°C, 进样速: 40 ms |
|
| 样品制备 |
|
方法一 |
|
|
50 mL 浓乙醇提取物 16 g 硅藻土涂层. 浆料用旋转蒸发器 40°C 干燥, 8 mbar, 打细粉并上3.3 cm × 40 cm 柱. 200 mL 乙酸乙酯和己烷混合物 (15: 85) 洗脱。另以30 mL 己烷过 8 g 硅胶过滤洗脱。 |
|
|
40 mL 己烷重新溶解干燥样品滤液以旋转蒸发器蒸发。4°C 保存过夜, 自由结晶, 过滤 ART 粗晶. 粗晶以10% 乙酸乙酯己烷混合物洗四次。剩余母液冷藏, 复苏 ART 结晶并按上述方法清洗。合并的结晶溶解、干燥。 |
|
|
甲醇和水热滤. 半纯化的 ART 重新溶解于热甲醇。逐滴将热水加入清 ART 溶液至浑。在加入少量甲醇。加入 50 mg 活性碳去色, 80°C 立即过滤与一温玻璃熔块覆盖的 1 g 硅藻土。清澈 ART 滤液缓慢蒸发得 ART 白色针晶。 |
|
|
方法二 |
|
|
65 g 黄花蒿 Artemisia 粉末以含 7% 乙酸乙醇上样 250 ml 不锈钢管机, 立即装入七个 1 cm 厚的玻璃面层. 前处理浸泡 2 小时达到提取标准. 剩余溶剂加入10 mL 在线暗盒以 SC-CO2 带入提取器. |
|
|
操作: 虹吸管式气缸液态CO2 (1) 通过283 K 冷水浴由注射器泵压缩到所需的工作压力 (4) 加热至盘管式换热器的超临界条件 (7). 超临界CO2 流入提取器 (8), 接触到粉末, 并提取青蒿素和莨菪亭入CO2 相. 温度控制器 (5), 温度检测器 (20), 压力计 (5) 控制所需温度压力. 提取物载有的CO2 气体进入第一吸收器 (13) 500 mL 乙醇降压填充。第二分离器填充500 mL 乙醇, 5 MPa, 303 K. 低压 CO2 气体放入湿式气体流量计 (16) 进入周围环境. 背压调节器中沉淀与乙醇提取部混合, 干燥溶剂, 溶于 2 ml 纯乙醇为 GC 和 HPLC 分析备用。50 ml 样品置入三螺旋, 循环烘箱 60°C (333 K) 干燥溶剂, 残留物称重 Mettler balance, 备用。 |
|
|
| 参考文献 |
|
[1]
|
Park, K. H., et al. (2012). "Artemisinin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interferon-β production in RAW 264.7 cells: Implications on signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 signaling and nitric oxide production." International Immunopharmacology 14(4): 580-584. |
|
[2]
|
Mueller, M. S., et al. (2000). "The potential of Artemisia annua L. as a locally produced remedy for malaria in the tropics: agricultural, chemical and clinical aspects." J Ethnopharmacol 73(3): 487-493. |
|
[3]
|
Firestone, G. L. and S. N. Sundar (2009). "Anticancer activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives." Expert Rev Mol Med 11: e32. |
|
[4]
|
Xiong, Z., et al. (2010). "Artemisinin, an anti-malarial agent, inhibits rat cardiac hypertrophy via inhibition of NF-κB signaling." European Journal of Pharmacology 649(1-3): 277-284. |
|
[5]
|
Kim, J.-T., et al. (2002). "In vitro antiprotozoal effects of artemisinin on Neospora caninum." Veterinary Parasitology 103(1-2): 53-63. |
|
[6]
|
Ploypradith, P. (2004). "Development of artemisinin and its structurally simplified trioxane derivatives as antimalarial drugs." Acta Tropica 89(3): 329-342. |
|
[7]
|
Adegoke, O., et al. (2012). "Highly sensitive liquid chromatographic analysis of artemisinin and its derivatives after pre-column derivatization with 4-carboxyl-2,6-dinitrobenzene diazonium ion." Acta Chromatographica 24(3): 445-462. |
|
[8]
|
Peng, C. A., et al. (2006). "Direct analysis of artemisinin from Artemisia annua L. using high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detector, and gas chromatography with flame ionization detector." J Chromatogr A 1133(1-2): 254-258. |
|
[9]
|
Liu, N. Q., et al. (2011). "A novel purification method of artemisinin from Artemisia annua." Industrial Crops and Products 34(1): 1084-1088. |
|
[10]
|
Tzeng, T.-C., et al. (2007). "EXTRACTION of scopoletin and artemisinin from Artemisia annua L." Separation and Purification Technology 56(1): 18-24. |
|
[11]
|
Gabriels, M. and J. Plaizier-Vercammen (2004). "Development of a reversed-phase thin-layer chromatographic method for artemisinin and its derivatives." J. Chromatogr. Sci. 42(7): 341-347. |
|
| 连结 |
 中药材图像数据库 中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库 药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库 中药标本数据库
|
 中药材图像数据库
中药材图像数据库
 药用植物图像数据库
药用植物图像数据库
 中药标本数据库
中药标本数据库