|
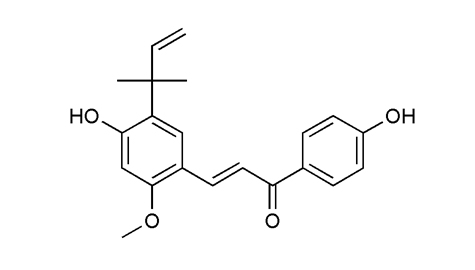
植物來源 |
|
|
生物活性 |
|
|
鑑定 |
熔點 |
101-102°C |
1HNMR

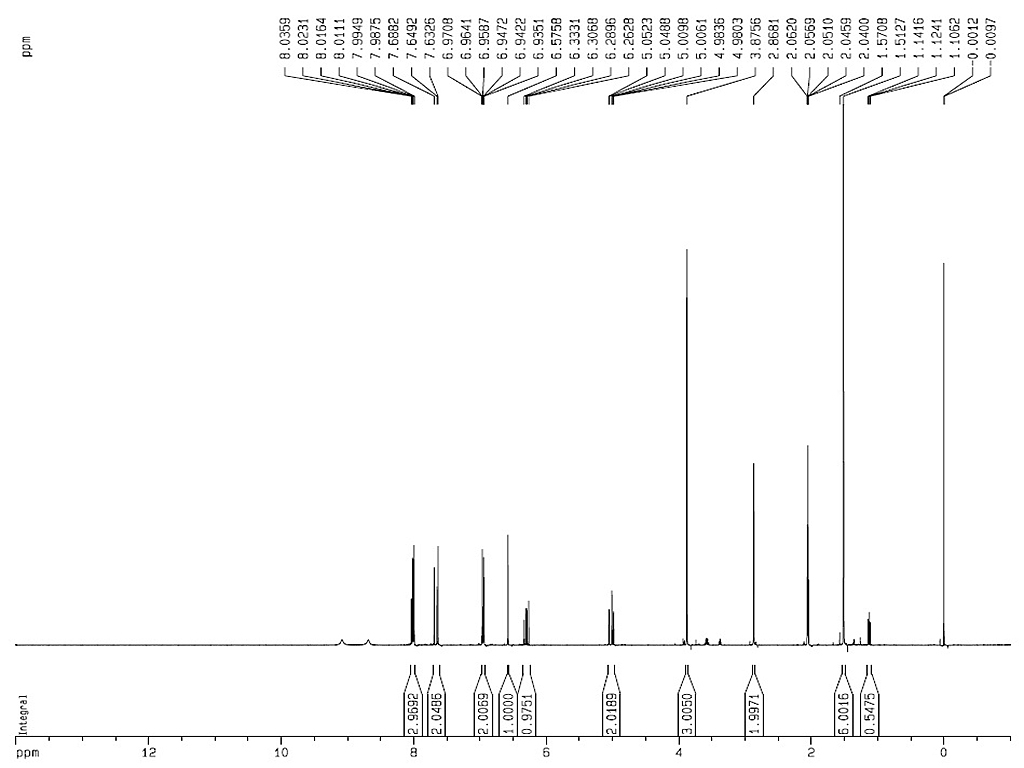
|
| 分析方法 |
|
| 儀器 |
預製60 F254 矽膠板, 0.2 mm thick (Merck) |
| 流動相 |
乙酸乙酯: 己烷: 甲酸 = 4: 4: 0.1 (v/v) 或正己烷: 乙酸乙酯: 乙酸 = 60: 45: 0.7 (v/v) |
| 檢測器 |
10% 硫酸噴淋加熱顯色 |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
CAMAG Linomat 5 半自動進樣器; 聚醯胺膜 |
| 流動相 |
0.23 mol/L SDS: 16% 正己烷: 11% 甲醇: 2.4% 正庚烷: 水 |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ366 nm |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
Hitachi Model D-2000 HPLC儀 |
| 色譜柱 |
TSKgel-C18 ODS-100Z 色譜柱 (150 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) |
| 流動相 |
A: 乙腈, B: 0.1% 甲酸, 0-10 min 15-20% A, 10-12 min 20-23% A, 12-26 min 23-23.7% A, 26-30 min 23.7-32% A, 30-50 min 32-52% A, 50-58 min 52-55% A, 58-63 55% A, 63-70 min 55-56% A, 70-85 min 56-80% A, 1.0mL/min |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ280 nm |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
HP1100 HPLC 儀 (Agilent, USA) |
| 色譜柱 |
Kromasil KR100-5C18 色譜柱, 150 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., Dalian Elite Analytical Instruments |
| 流動相 |
A: 乙腈, B: 0.05% 三氟乙酸, 0-5 min 20-40% A, 5-10 min 40-50% A, 10-25 min 50% A, 25-35 min 50-80% A, 0.8 mL/min |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ254 nm 合 364 nm |
|
|
|
| 儀器 |
An Agilent 1200 HPLC 系統 (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany), 包括二元泵, 二極管數組檢測器, 自動進樣器, 恒溫柱溫箱 |
| 色譜柱 |
Agilent Zorbax SB-C18 色譜柱 (50 × 4.6 mm, 1.8 µm), 30°C |
| 流動相 |
A: HCOOH: H2O (0.2: 100, v/v), B: ACN, 0-4 min 19% B, 4-11 min 19-27% B, 11-17 min 27-38% B, 17-23 min 38-55% B, 23-25 min 55% B, 25-28 min 55-65% B, 28-30 min 65% B, 30-36 min 65-100%, 0.7 mL/min, 進樣量: 1 µL |
| 檢測器 |
UV λ190 nm 至 400 nm; Agilent 6530 Q-TOF 質譜儀及 ESI 接口和 Agilent MassHunter Acquisition 軟件Ver. A.01.00, MassHunter 工作站Version B.02.00, 乾燥氣: N2, 柳綠: 5.0 L/min, 乾燥氣溫: 325°C, 霧化氣: 45 psig, 鞘氣溫度: 400°C, 鞘氣流: 12 L/min, 毛細管: 3500 V, 撇渣器: 65 V, OCT RF V: 750 V, 碎片: 100 V, 碰撞能: 5-35 V, 正負離子模式, 質譜範圍: m/z 100-1700 |
|
| 樣品製備 |
|
方法一 |
|
|
乙醇-水 (95: 5) SK3200LH 超聲儀超聲提取三次 (Shanghai Kudos Ultrasonic Instrument Co., Shanghai, China). Model SENCO R-201 旋轉蒸發器合併濃縮 (Shanghai Shensheng Biotech Co., Shanghai, China). 2% 氫氧化鈉溶解, 真空過濾. Hangxhou Xinhua Paper Industry (Hangzhou, China) 濾紙過濾. 2% 鹽酸溶液酸化. 冷水沖洗, Model FD-1 凍幹機凍幹 (Beijing Boyikang Technology, Beijing, China). HSCCC 分離: 下相正己烷-氯仿-甲醇-水 (5: 6: 3: 2, v/v) 流動相1.8 mL/min, 800 rpm, UV 254 nm. 收集餾分, HSCCC 再純化. |
|
|
Model TBE-300A HSCCC 儀, Tauto Biotech Co., Shanghai, China 配備恒溫外套的多層螺旋星式離心, Model S1007 恒流泵 (Beijing Shengyitong Technology Development, Beijing, China), Model 8823A UV 檢測器 (Beijing Institute of New Technology Application), 手動進樣閥及 20 ml 回路, Model 3057 便攜收集器 (Sichuan Instrument Factory, Chongqing, China) 和 Model Sepu3000 色譜數據工作站Hangzhou Puhui Scientific Technology. |
|
|
下相正己烷-氯仿-甲醇-水 (1.5: 6: 3: 2, v/v) |
|
|
1.5mL/min; 800rpm |
|
|
UV λ254 nm |
|
|
方法二 |
|
|
樣品粉末 70% 乙醇提取三次, 2 小時. 過濾, 蒸幹. |
|
|
水中溶, CH2Cl2, EtOAc, 和 n-butanol 分離. DPPH-HPLC-MS 篩選分離. EtOAc 部備用. |
|
|
EtOAc 提取物過矽膠柱 (2.0 kg, 100-200 mesh, 10 × 100 cm), CH2Cl2-MeOH (60:1 - 1:1, v/v) 為流動相. 餾分 34-41, CH2Cl2-MeOH = 30: 1 (v/v) 洗脫, 過矽膠柱 (200 g, 200-300 mesh, 3.5 × 60 cm) 石油醚-EtOAc 梯度洗脫 (10:1 - 1:1, v/v). 餾分75-95 結晶, CH2Cl2-MeOH (2:1, v/v) 洗脫, 甲醇中得目標化合物. |
|
|
方法三 |
|
|
乙酸乙酯室溫提取三次. 合併, 真空濃縮. |
|
|
乙酸乙酯溶解, 以正己烷洗脫分離. 過矽膠柱 (5.0 × 45.0 cm) 乙酸乙酯/正己烷 (1: 2) 得到 8 餾分 (A-H). |
|
|
餾分 H 過 RP-18 矽膠柱, 甲醇/水洗脫 (1.5: 1) UV 檢測, 285 nm 流速 5 mL/min. |
|
|
| 參考文獻 |
|
[1]
|
Fu, Y., et al. (2013). "Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of six flavonoids separated from licorice." Food Chemistry 141(2): 1063-1071. |
|
[2]
|
Furuhashi, I., et al. (2005). "Inhibition by licochalcone A, a novel flavonoid isolated from liquorice root, of IL-1beta-induced PGE2 production in human skin fibroblasts." J Pharm Pharmacol 57(12): 1661-1666. |
|
[3]
|
Chu, X., et al. (2013). "Attenuation of allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma by Licochalcone A." Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. |
|
[4]
|
Chu, X., et al. (2012). "Licochalcone a inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo." J Agric Food Chem 60(15): 3947-3954. |
|
[5]
|
Rafi, M. M., et al. (2000). "Modulation of bcl-2 and cytotoxicity by licochalcone-A, a novel estrogenic flavonoid." Anticancer Res 20(4): 2653-2658. |
|
[6]
|
Yuan, X., et al. (2013). "Licochalcone a-induced human bladder cancer t24 cells apoptosis triggered by mitochondria dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress." Biomed Res Int 2013: 474272. |
|
[7]
|
Kim, Y. J., et al. (2013). "Licochalcone A Enhances Geldanamycin-Induced Apoptosis through Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Caspase Activation." Pharmacology 92(1-2): 49-59. |
|
[8]
|
Xiao, X.-y., et al. (2011). "Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis." Cancer Letters 302(1): 69-75. |
|
[9]
|
Fu, Y., et al. (2004). "Licochalcone-A, a novel flavonoid isolated from licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra), causes G2 and late-G1 arrests in androgen-independent PC-3 prostate cancer cells." Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 322(1): 263-270. |
|
[10]
|
Kim, Y. H., et al. (2010). "Antiangiogenic effect of licochalcone A." Biochem Pharmacol 80(8): 1152-1159. |
|
[11]
|
Li, Y.-J., et al. (2011). "Screening and characterization of natural antioxidants in four Glycyrrhiza species by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry." Journal of Chromatography A 1218(45): 8181-8191. |
|
[12]
|
Hao, H., et al. (2013). "Effect of Licochalcone A on Growth and Properties of Streptococcus suis." PLoS One 8(7): e67728. |
|
[13]
|
Kim, S. N., et al. (2008). "Licochalcone A inhibits the formation and bone resorptive activity of osteoclasts." Cell Biology International 32(9): 1064-1072. |
|
[14]
|
Won, S.-R., et al. (2007). "Licochalcone A: A lipase inhibitor from the roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis." Food Research International 40(8): 1046-1050. |
|
[15]
|
Cui, S., et al. (2007). "Identification of Radix Glycyrrhizae by microemulsion thin-layer chromatography." Zhongcaoyao 38(4): 540-542. |
|
[16]
|
Zhang, J., et al. (2012). "Flavonoids content in Licorice residue determined by HPLC." Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Keji 19(3): 233-234. |
|
[17]
|
Wang, Q.-E., et al. (2004). "Isolation and purification of inflacoumarin A and licochalcone A from licorice by high-speed counter-current chromatography." Journal of Chromatography A 1048(1): 51-57. |
|
| 連結 |
 中藥材圖像數據庫 中藥材圖像數據庫
 藥用植物圖像數據庫 藥用植物圖像數據庫
 中藥標本數據庫 中藥標本數據庫
|
 中藥材圖像數據庫
中藥材圖像數據庫
 藥用植物圖像數據庫
藥用植物圖像數據庫
 中藥標本數據庫
中藥標本數據庫


